 0
0








 0
0









For high-bandwidth applications in large data centers, 5G communications, and space-grade applications such as satellites, there is a huge demand for miniaturized power supplies. Due to the limited on-board space for embedded applications, enterprises need small power supplies with higher power density. Thus, depending on the application, the power density can be understood from different perspectives, but the ultimate goal remains the same, which is to reduce the size and thus increase the power density.
Thermal performance has always been one of the limiting factors for increasing power density. The right integrated circuit (IC) package is important to easily drain heat from the system. This allows the system not to see any unreasonable temperature increases, and these power losses are tolerable. The goal here is thermal optimization of IC packages and printed circuit boards (PCBS) to reduce temperature rise in the presence of power converter losses. The design trend of miniaturized converters makes system-level thermal design with smaller silicon wafers and package sizes difficult. The thermal resistance of PN junction to the environment will deteriorate exponentially with the reduction of the bare area.
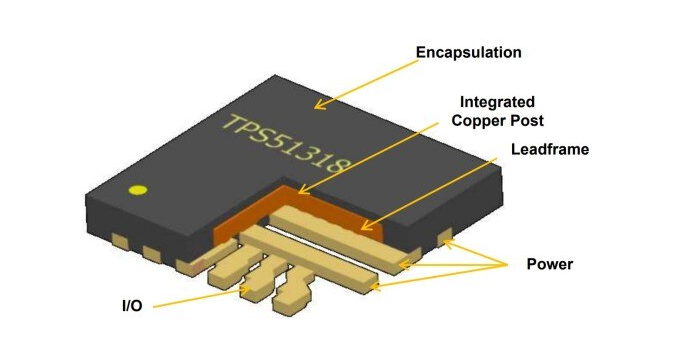
To easily remove heat from the IC, Texas Instruments (TI) has invested in the development of the HotRod package, which replaces the split-line square Flat pin-less package (QFN) with a flip-chip type package. The results show that the inductance of the parasitic loop is significantly reduced due to the QFN package, while maintaining good thermal performance. One challenge with HotRod packages, however, is the difficulty of building large bare strip attachment pads (DAP) that help improve package heat dissipation. To address this issue, TI proposed an enhanced HotRod QFN that enables a package with a large DAP while maintaining existing advantages.
Figure 1: HotRod QFN structure and bare piece bonding
How to achieve more power in a smaller space?
The design trend for high power density has been around for decades, and industry manufacturers expect this trend to continue in the future. With the advancement of technology, the size of the power supply with high power output capacity has been greatly reduced. Research and development to improve power density complement other areas such as energy efficiency and manufacturing costs. TI has done a lot of work to achieve more power in a smaller space, and is also designing ics for aerospace applications
Figure 2: The size of the power module has decreased over time

Which are high power density buck converters for aerospace applications?
TI's TPS566242 High power density synchronous buck converter supports input voltages from 3V to 16V and continuous currents up to 6A. The small, cost-effective SOT563 package and integrated bootstrap capacitor design are designed to serve a wide range of applications, including broadband monitoring, enterprise machines, data centers and distributed power systems. This easy-to-use high power density and efficient buck converter uses the D-CAP3 topology to provide fast transient response and support low ESR output capacitors without external compensation. Interestingly, the circuit design has two ground, namely GND and AGND, which need to be connected together for optimal thermal performance.
The ECO mode of this model enables the IC to remain efficient even under light loads. But another model, the TPS566247, operates in FCCM mode, which maintains the same frequency and low output ripple under all load conditions. The switching frequency of the IC is fixed at 600kHz. This switching frequency affects the performance of the buck converter and is considered a very important parameter. A TI report suggests that the impact of switching frequency on buck converter performance can be seen in terms of efficiency, heat dissipation, ripple and transient response.
Figure 3: High power density synchronous buck converter TPS566242

For aerospace applications, TI highlights two space-grade buck converters: TPS7H4001-SP and TPS50601A-SP. The TPS7H4001-SP is a radiation-resistant synchronous buck converter with integrated low-resistance MOSFETs. The IC has an input voltage of 3V to 7V and a current supply of up to 18A. The DC/DC converter features a tunable internal oscillator from 100 KHZ to 1MHz, providing a range of benefits for aerospace use cases. The high output current capability at such a small size can be used to power high-current FPgas and ASIC core voltage rails. The operation of the TPS7H4001-SP does not require an external clock, which is a huge advantage for aerospace embedded systems.
Another space-grade buck converter is the TPS50601A-SP, which is also A radiation-resistant platform with 7 V, 6 A synchronous buck capability and optimized for small designs. The buck converter has high efficiency and integrates both high and low side MOSFETs. The number of components is reduced through current mode control and the inductor package size is reduced through high switching frequencies. The IC is available in a small-size, heat-enhanced 20-pin ceramic flat package.
Figure 4: Space grade buck converter

Conclusion
Due to space constraints, electronics everywhere, from consumer devices to satellites in space, need to deliver higher power at a smaller size. Research and development over the past decade to further reduce the size of the power supply has found a way through a variety of technologies. TI and other semiconductor companies are designing and manufacturing robust and safe buck and boost converters using GaN and SiC technologies.
Especially for aerospace applications, launching applications in space requires a combination of power supply and thermal management design, which has become challenging. This is because thermal performance directly affects efficiency. Semiconductor companies are now taking the necessary steps to design high power density synchronous buck converters for aerospace applications.
Heisener Electronic is a famous international One Stop Purchasing Service Provider of Electronic Components. Based on the concept of Customer-orientation and Innovation, a good process control system, professional management team, advanced inventory management technology, we can provide one-stop electronic component supporting services that Heisener is the preferred partner for all the enterprises and research institutions.
